Abstract
Background:
NPM1 mutations (NPM1 +) occur in ~30% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), often with co-occurring mutations including isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations (IDH +). Previous studies suggest early acquisition and expansion of IDH1/2 mutations (IDH1 +/IDH2 +) prior to NPM1 + development increase relapse risk. Yet the clonal hierarchy of NPM1 +/IDH + AML, dynamics of IDH + during therapy, and predictive value of IDH1 +/2 + in NPM1 + AML in response to standard intensive (IC) or venetoclax-based (VEN) treatment is less studied.
Methods:
We identified 71 patients with newly diagnosed NPM1+ AML (index cohort). Longitudinal molecular assessment of bone marrow samples at diagnosis, remission, and relapse was performed using next-generation sequencing (NGS) of genes frequently mutated in AML. Clonality within each sample was inferred using variant allele frequency (VAF) of individual mutations compared with NPM1 +(co-dominant: VAF difference of < 10%; sub-clonal: VAF ≥10% lower). Measurable residual disease (MRD) was assessed using flow cytometry (FC) (MRD FC; lower limit of sensitivity 10 -3-10 -4) and NGS. To validate findings in the index cohort, clinical and genomic data were collected from a publicly available dataset of 39 patients with NPM1 + AML who underwent single cell DNA sequencing (scDNAseq) at our institution. Categorical and continuous variables were assessed using the fisher exact test and the Wilcoxon rank sum test, respectively. Adjustment for multiple comparisons utilized the Benjamini-Horchberg procedure. Time-to-event outcomes were assessed by the log-rank method.
Results:
Median patient age was 64 years (range 19-84). Thirty-eight patients (54%) received IC (IC: n=30, IC+VEN: n= 8); 33 (46%) received lower-intensity therapy (lower-intensity: n= 6, lower-intensity+VEN: n=27). Common co-occurring mutations at diagnosis included DNMT3A (62%), FLT3 (52%), TET2 (27%), IDH2 (23%), IDH1 (18%), PTPN11 (18%), and NRAS (17%).
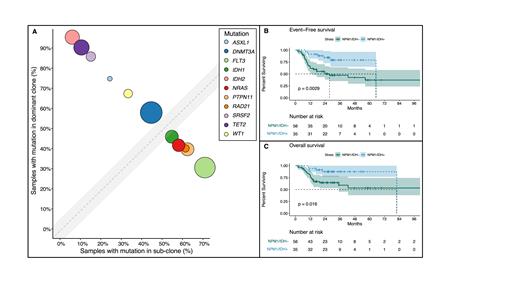
SRSF2, IDH2, TET2, ASXL1, and DNMT3A mutations preceded or were co-dominant with NPM1 +, while NRAS, PTPN11, and FLT3 mutations were sub-clonal. IDH1 +was sub-clonal in 40% of cases (Fig. 1A). In the scDNAseq cohort IDH1 + was sub-clonal in 40% (n=3/8); IDH2 + preceded NPM1 +in 75% (n=9). Compared with IDH1 +, IDH2 + was more likely to precede or be co-dominant with NPM1 + (95% vs. 60%, p-value: 0.017).
DTA (DNMT3A, TET2, ASXL1) mutations were detected more often in remission versus IDH + (88% vs. 55%, p-value: 0.01). Persistent IDH1 + and IDH2 + were identified in 36% (n=4) and 73% (n=11) of patients. Concurrent MRD FC confirmed clearance of the previous AML clone in 100% of patients, with a pre-leukemic/CH immunophenotype identified in 50% and 80% of cases with persistent IDH1 +or IDH2 +, respectively
Patients with IDH + often developed new or persistent mutations in remission compared with patients with wild-type IDH(54% vs. 12%, p-value <0.001), including splicing mutations (SRSF2, U2AF1, ZRSR2, SF3B1: 25% [n=7]) and emergent TET2 mutations (14% [n=4]). Despite persistence of these mutations in remission, 100% achieved MRD FC negativity and all remain in remission, however 80% had a a CH phenotype detectable by FC.
Patients with NPM1 +/IDH + compared with NPM1 +/IDH - AML in complete remission (N=91) had improved event-free (EFS; median 65 vs. 28 months, p-value: 0.002) and overall survival (OS; median 82 months vs. NR, p-value: 0.02) (Fig. 1B and C), largely driven by NPM1 +/IDH2 + cases, and patients receiving IC. No survival difference was observed based on clonal hierarchy of IDH + (clonal vs sub-clonal) compared with NPM1 + or persistent IDH + in remission with concurrent clearance of NPM1 + and MRD FC. FLT3 mutations were identified at similar frequencies in the NPM1 +/IDH +and NPM1 +/IDH - groups (50% vs. 53%, p-value: 0.84; ITD: 81% vs. 69%, p-value: 0.49), and a similar number of patients receiving VEN (48% vs.43%, p-value: 0.38).
Conclusion:
IDH1 + and IDH2 + develop at differing timepoints during leukemogenesis in NPM1 + AML. IDH2 + frequently precedes NPM1 and persists in remission, while IDH1 + is more often sub-clonal and cleared in remission. Persistent IDH1 + or IDH2 + frequently correlate with detection of a CH phenotype by MFC in remission, and in the absence of NPM1 + and MRD FC do not influence relapse. Improved EFS and OS was observed with NPM1 +/IDH + AML, identifying a molecular subgroup associated with favorable outcomes to both VEN and IC treatment regimens
DiNardo: Foghorn: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; GlaxoSmithKline: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ImmuneOnc: Honoraria, Research Funding; Notable Labs: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios/Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Forma: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb company: Honoraria, Research Funding. Wang: Stemline Therapeutics: Honoraria. Kadia: Ascentage: Other; AstraZeneca: Other; Liberum: Consultancy; Genfleet: Other; Pfizer: Consultancy, Other; Astellas: Other; Novartis: Consultancy; BMS: Other: Grant/research support; Jazz: Consultancy; Dalichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy, Other: Grant/research support; Cure: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Other: Grant/research support; Aglos: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Other: Grant/research support; Cellonkos: Other; Sanofi-Aventis: Consultancy; Pulmotech: Other. Daver: Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; FATE Therapeutics: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Hanmi: Research Funding; Sevier: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Research Funding; Trovagene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Trillium: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novimmune: Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Other: Data Monitoring Committee member; Dava Oncology (Arog): Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Syndax: Consultancy; Shattuck Labs: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; SOBI: Consultancy; STAR Therapeutics: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Newave: Research Funding. Short: NGMBio: Consultancy; Takeda Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Astellas: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Khoury: Angle: Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding. Konopleva: F. Hoffmann-La Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: grant support; Agios: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Calithera: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Ascentage: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights, Research Funding; Rafael Pharmaceuticals: Other: grant support, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Grant Support, Research Funding; KisoJi: Research Funding; Sanofi: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Forty Seven: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Cellectis: Other: grant support; Novartis: Other: research funding pending, Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights; Ablynx: Other: grant support, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Reata Pharmaceuticals: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: grant support, Research Funding. Ravandi: AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Xencor: Honoraria, Research Funding; Taiho: Honoraria, Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz: Honoraria, Research Funding; Prelude: Research Funding; Syros Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria. Takahashi: Celgene/BMS: Consultancy; Symbio Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Loghavi: Abbvie: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Curio Sciences: Honoraria; Gerson Lehrman Group: Consultancy; Guidepoint: Consultancy; Peerview: Honoraria; Qualworld: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal